Today we're releasing ScrapeGraphAI 100k — a dataset of ~100,000 real-world structured extraction examples derived from 9 million PostHog events collected from the ScrapeGraphAI open-source library during Q2-Q3 2025.
The dataset is on hugging face 🤗
TL;DR + What's in Each Row
So our open source library uses LLMs to extract structured data from web pages. In a nutshell; Webpage markdown + user defined JSON schema in -> json out from the LLM.
We've been collecting anonymized telemetry (with user consent) to understand how people use the library. Learn more about how we use PostHog for analytics. We had around 9 million events.
This isn't synthetic data. These are real prompts, real schemas, real web content, and real LLM responses from real usage.
From 9M Events to 100k Examples
We started from 9M events collected from PostHog, then we clean it into two steps:
Step 1: Extract and Compute Metrics
Each PostHog event has the prompt, schema, response, source content, model used, and execution time nested inside other values. We pulled these fields out and computed some extra metrics for each schema:
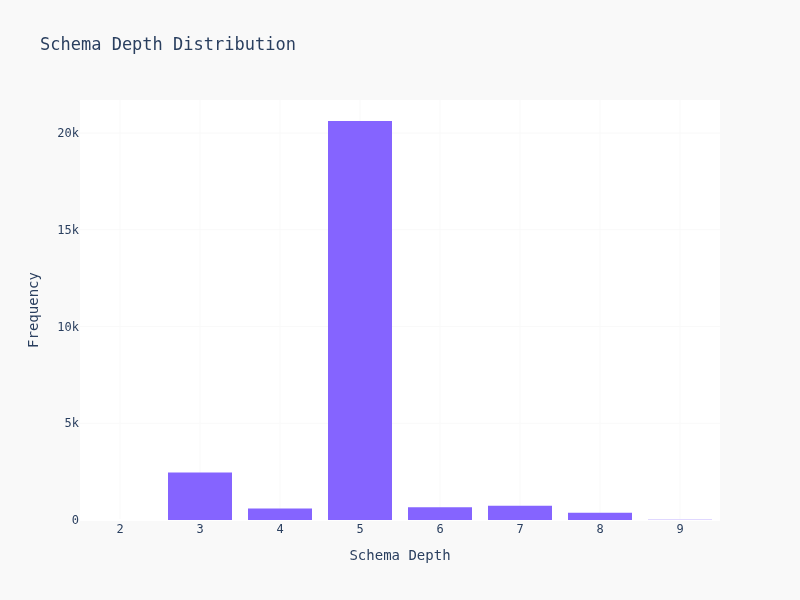
- Schema depth: How deep the nesting goes
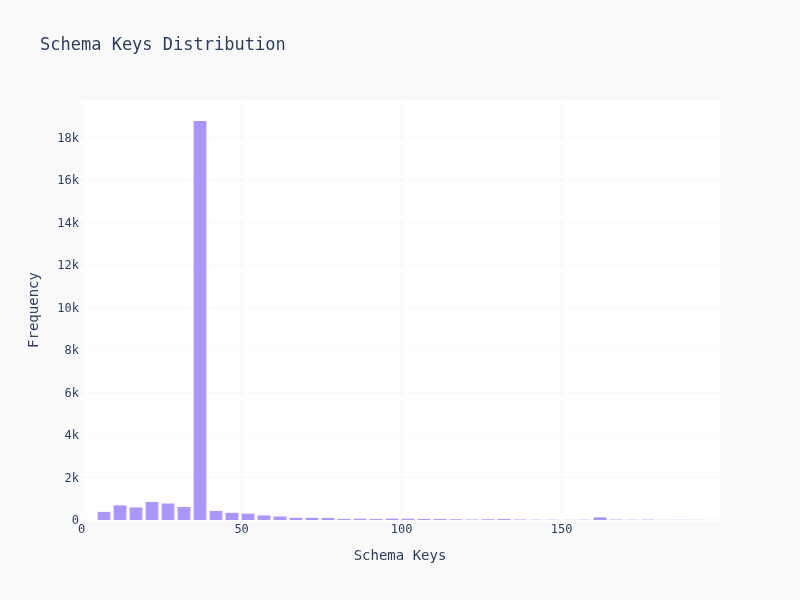
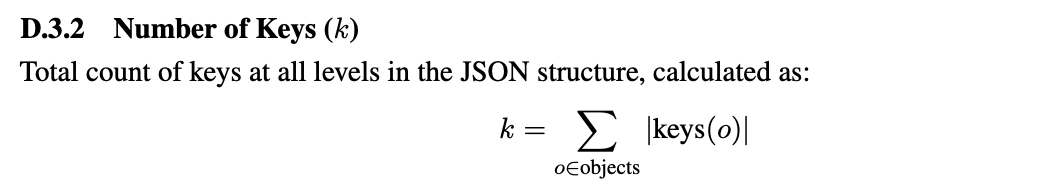
- Schema keys: How many fields to extract
- Schema elements: Total structural pieces
- Cyclomatic complexity: Branching shit from
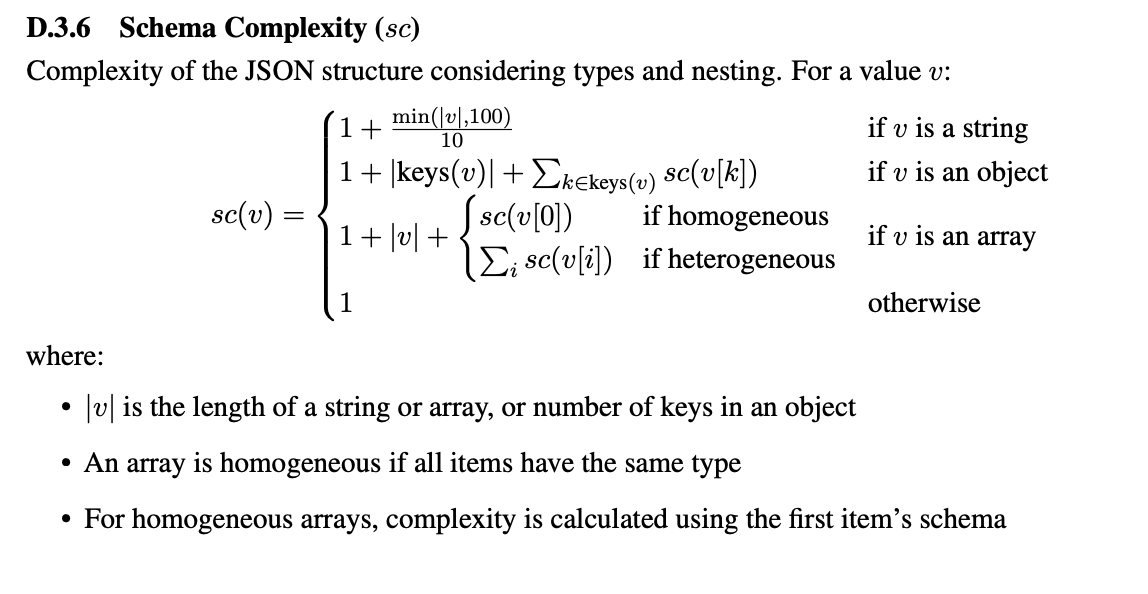
oneOf,anyOf, etc. - Complexity score: Weighted combo of all the above
These metrics should help us understanding how "hard/difficult" is a schema, they come from SLOT: Structuring the Output of Large Language Models (Wang et al., 2025). For example, the more nested a schema is, the more difficult - at least in theory. For more on working with structured output and schemas, check out our guide. We'll find out all these metrics are highly correlated and mostly useless; we could have just computed the number of keys tbh.
We also validated each response against its schema using jsonschema-rs to get response_is_valid. This tells you when the LLM fucked up; avg validity is 93%. Almost 90% of the times people used gpt-4o-mini.
Step 2: Balance by Schema
Some schemas showed up hundreds of thousands of times, others appeared once making the dataset heavily unbalanced. For example, two chinese schemas were used 5M times out of the 9M data we had 😅.
The fix was simple: for each unique schema hash, keep max 5 randomly selected examples from different source URLs. This makes the dataset more balanced across different extraction tasks.
Result: From 9M down to ~100k balanced examples across the full spectrum of extraction tasks we had. Which is what we wanted.
Dataset Statistics
We computed some stats to understand what is going on inside.
Schema Complexity Distribution
depth is computed as:
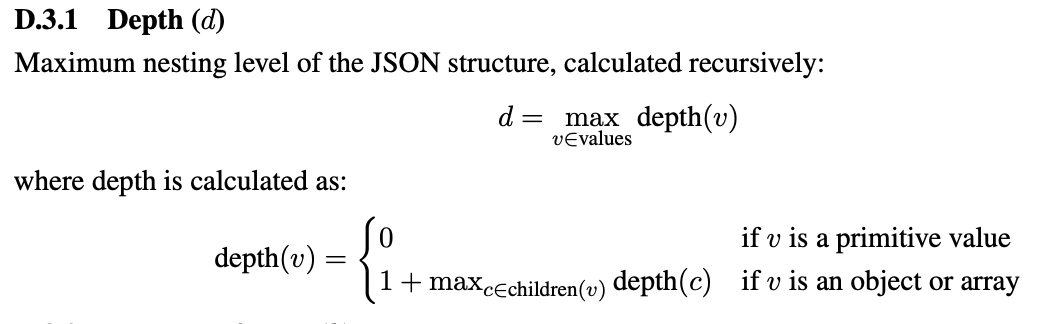
keys is computed as:
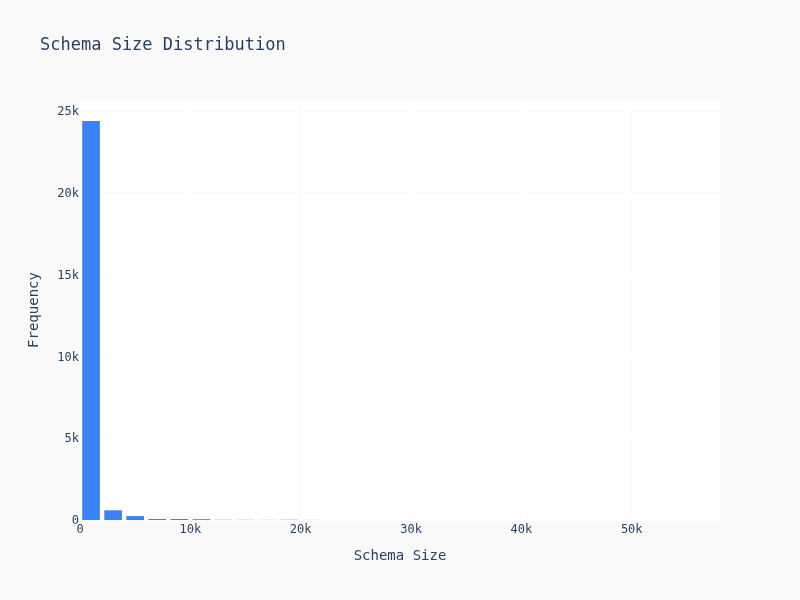
schema size, very easy, size = len(json.dumps(schema).encode("utf-8))
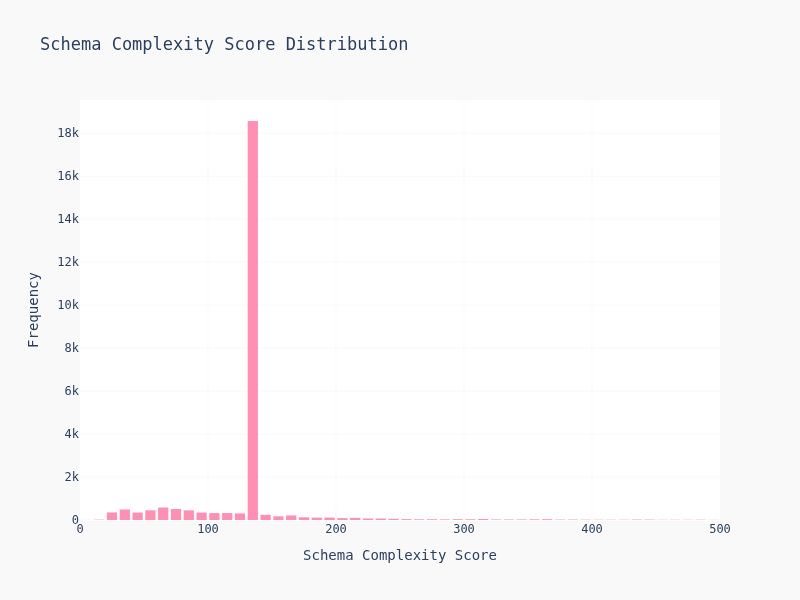
complexity:
Most schemas are simple — 2-4 levels deep, 5-15 keys. But there's a long tail of gnarly schemas with deep nesting and dozens of fields. Suprisily enough, most of them are cluster together and creates the weird looking dildo graph.
Response Size Distribution
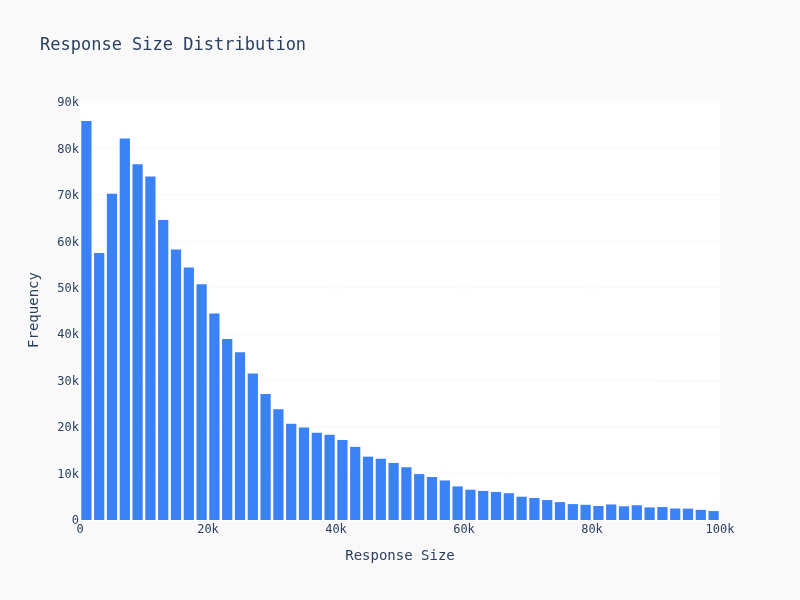
Response sizes are all over the place. Simple price extraction? 50 bytes. Full article with metadata? 50KB. This diversity reflects the wide range of use cases, from price monitoring to real estate scraping to market research.
Percentile Analysis
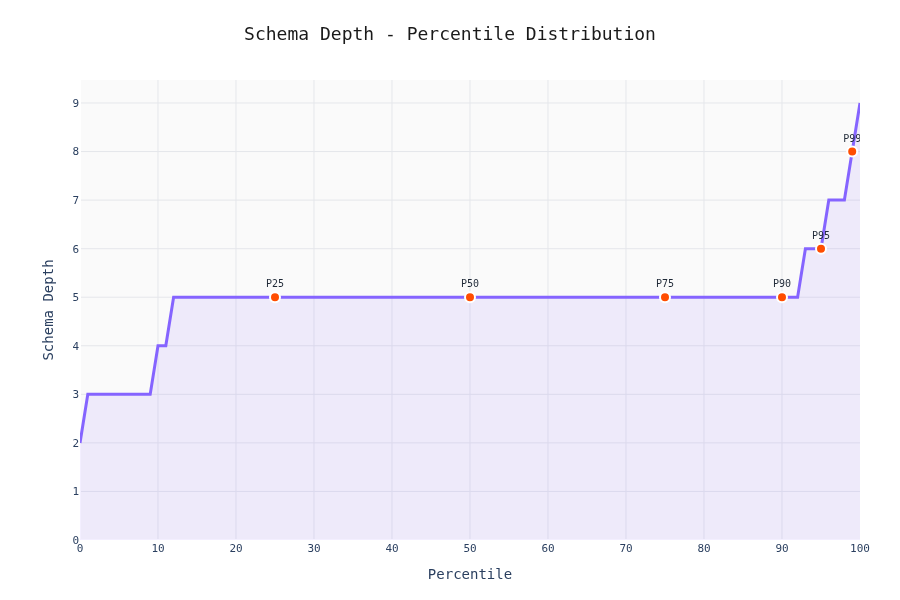
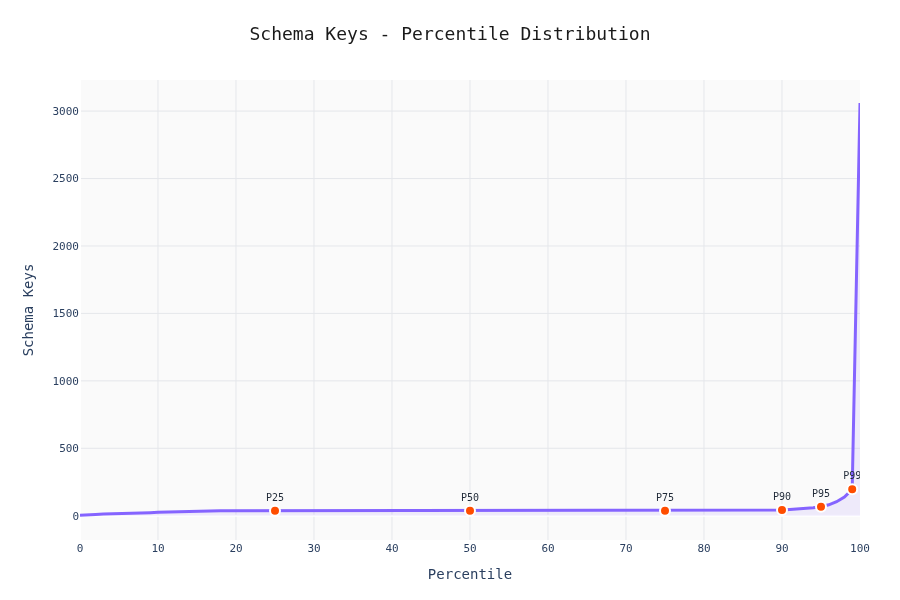
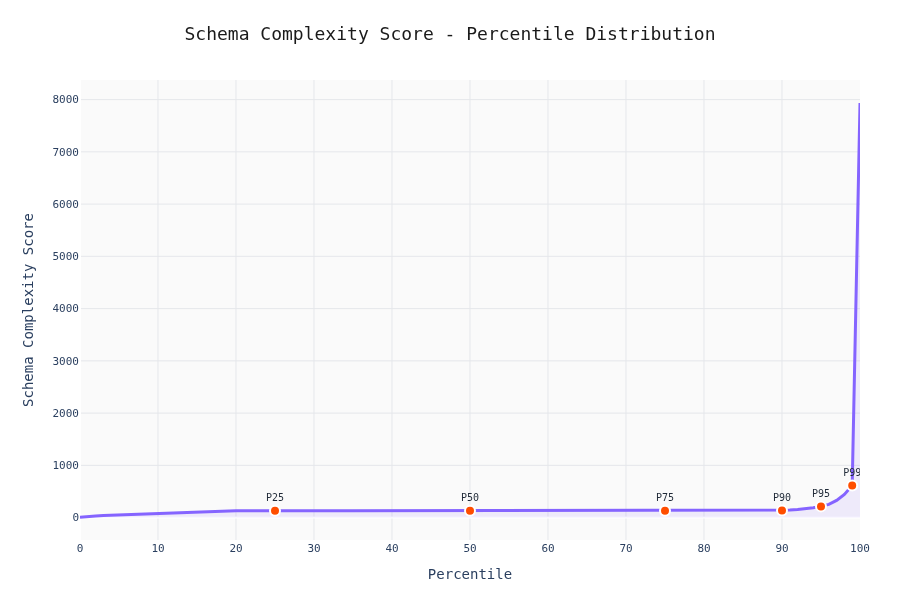
90% of schemas have <20 keys and depth <5. The other 10% is where LLMs start sweating.
Validation Rate vs. Schema Complexity
The interesting part. Does schema complexity affect whether the LLM produces valid output?
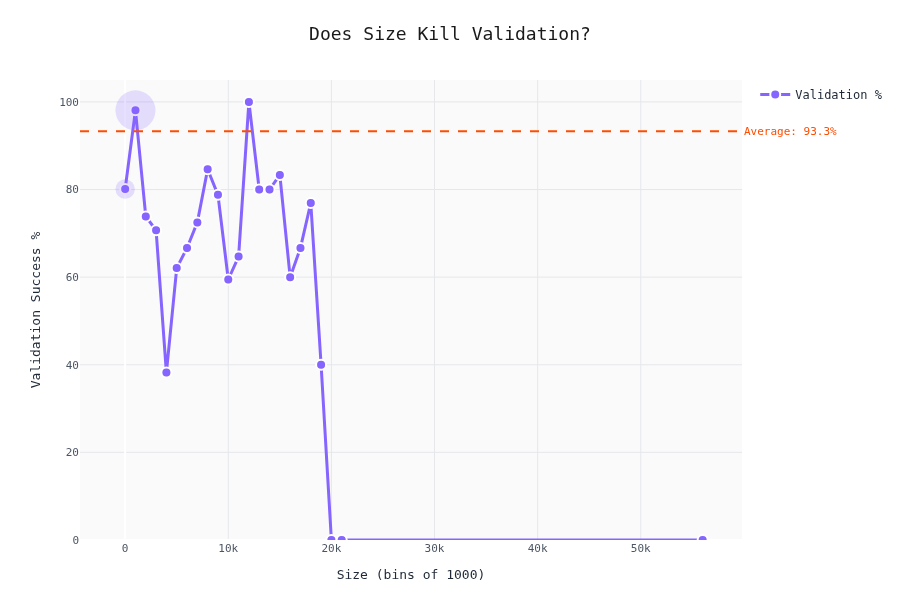
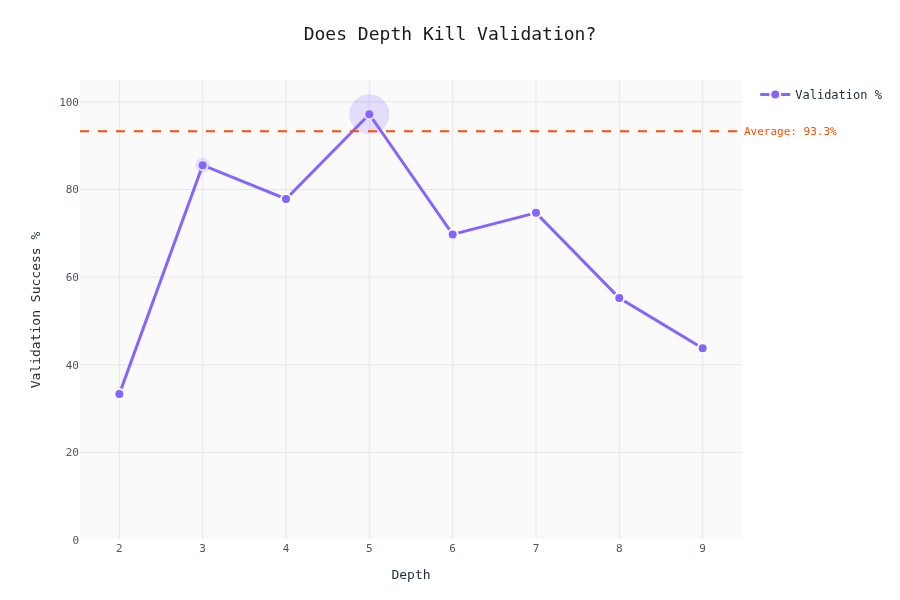
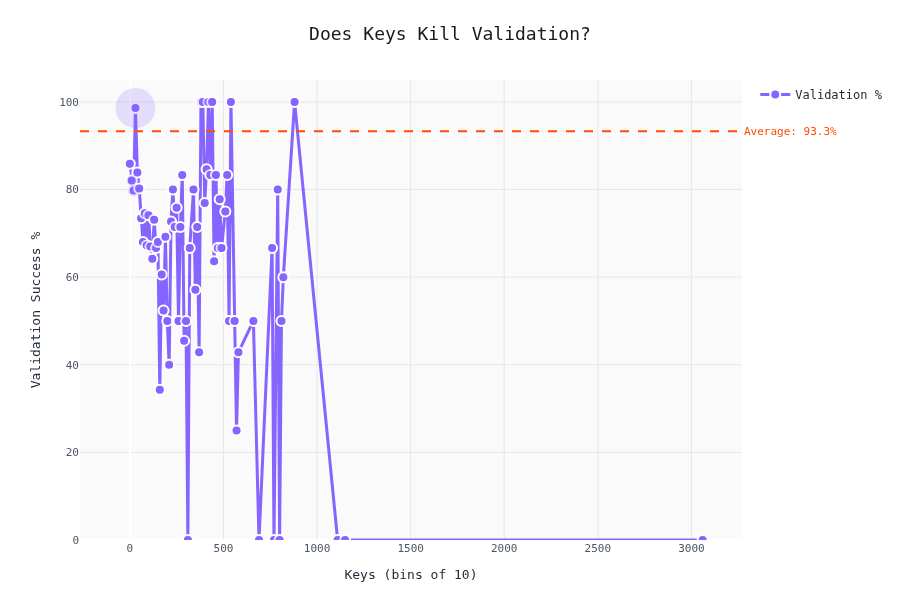
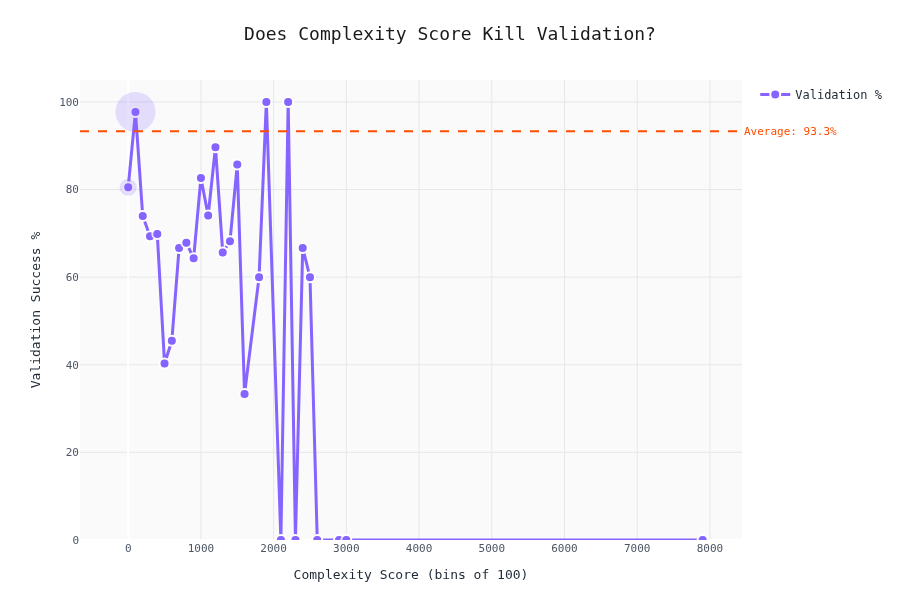
The drop-off isn't linear — there are thresholds where LLMs start failing hard. To be honest; we cannot really tell here. My gut felling is that the validaty depends by the difficulty of the content as well; we don't have a metric for that one (yet).
Correlation Matrix
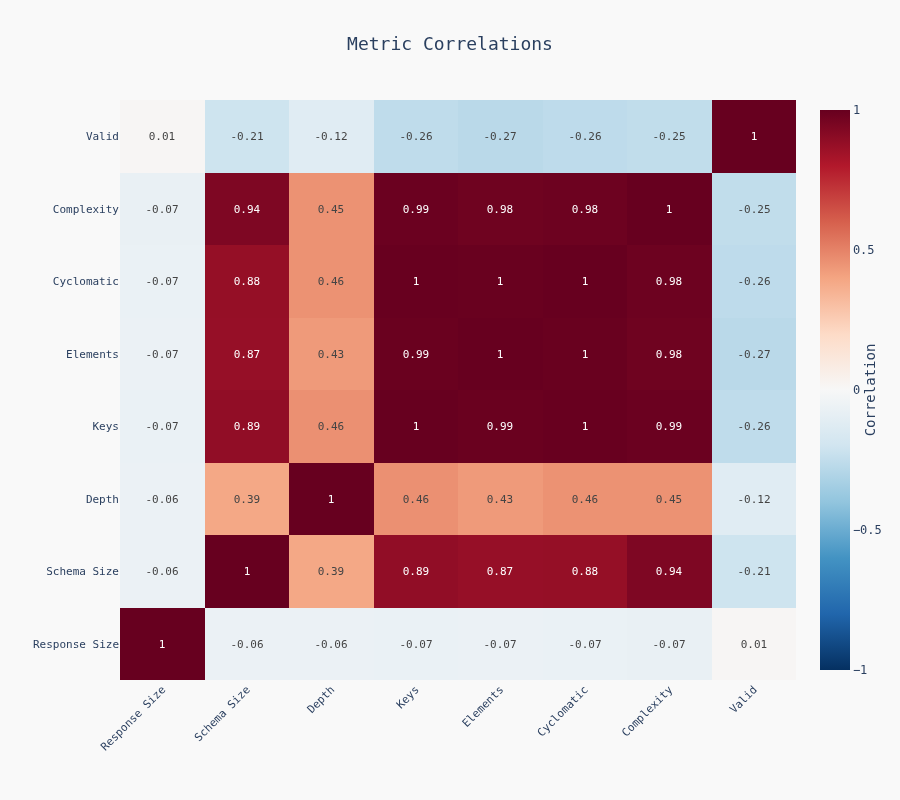
Schema metrics correlate with each other (complex in one dimension = complex in others). Execution time correlates with response size. No surprises.
What's In Each Row
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
prompt |
Full prompt sent to the LLM |
schema |
JSON schema defining expected output |
schema_hash |
SHA256 for deduplication |
response |
What the LLM actually returned |
content |
Source web content |
llm_model |
Which model was used |
source |
Source URL |
execution_time |
How long it took |
response_size |
Response size in bytes |
schema_* |
Complexity metrics |
response_is_valid |
Did the response match the schema? |
response_is_valid is clutch. Filter for successes or failures depending on what you need.
Limitations
Real-world data = messy data:
- Some responses are truncated or malformed
- Web content may reference external resources not included
- Validation is syntactic only — semantically wrong but valid JSON passes
- This reflects ScrapeGraphAI usage patterns, not general LLM usage
Get the Dataset
The dataset is on hugging face 🤗
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("scrapegraphai/scrapegraphai-100k")Citation
@dataset{scrapegraphai_2025_100k,
title = {ScrapeGraphAI 100k Structured Output Dataset},
author = {Francesco Zuppichini},
year = {2025},
email = {francesco@scrapegraphai.com},
url = {https://huggingface.co/datasets/scrapegraphai/scrapegraphai-100k}
}Big thanks to William Brach for the help and feedbacks for this blog post 🫶
Built by the ScrapeGraphAI team. Questions? francesco@scrapegraphai.com
Related Resources
Want to learn more about structured data extraction and AI-powered web scraping?
- Prompt Engineering Guide - Master the art of writing effective prompts for data extraction
- Structured Output Guide - Learn how to use schemas for consistent data extraction
- Mastering ScrapeGraphAI - Complete guide to using ScrapeGraphAI endpoints
- AI Agent Web Scraping - Discover how AI agents revolutionize data collection
- PostHog Analytics - Learn how we use PostHog for product analytics
- Production Web Scraping Best Practices - Scale your scraping operations