YouTube Data Scraping: The Complete Guide for 2025
Learn how to extract valuable data from YouTube using ScrapeGraphAI. This guide covers everything from basic scraping concepts to implementing advanced data extraction techniques for video analytics.

Web scraping is a powerful technique that allows you to extract data from websites automatically. When it comes to YouTube, scraping can provide invaluable insights for content creators, marketers, and data analysts.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll show you how to scrape YouTube data using ScrapeGraphAI, a robust tool that simplifies extracting valuable information even from complex pages. Whether you're looking to scrape YouTube videos, channels, or comments, this guide has you covered.
What is YouTube Scraping?
YouTube scraping involves programmatically accessing YouTube pages and extracting the desired information. It's an invaluable technique for data analysis, trend monitoring, and competitive intelligence. Remember to always scrape YouTube ethically and adhere to YouTube's terms of service.
Why Scrape YouTube Data?
YouTube is one of the largest video platforms globally, making it a treasure trove of insights:
- Trend Analysis: Discover which videos are gaining traction and what content resonates with audiences.
- Content Optimization: Understand what video titles and formats drive viewer engagement.
- Competitive Intelligence: Analyze competitors' strategies to refine your own content approach.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Leverage real-time data to enhance marketing and content strategies.
How to Scrape YouTube with ScrapeGraphAI
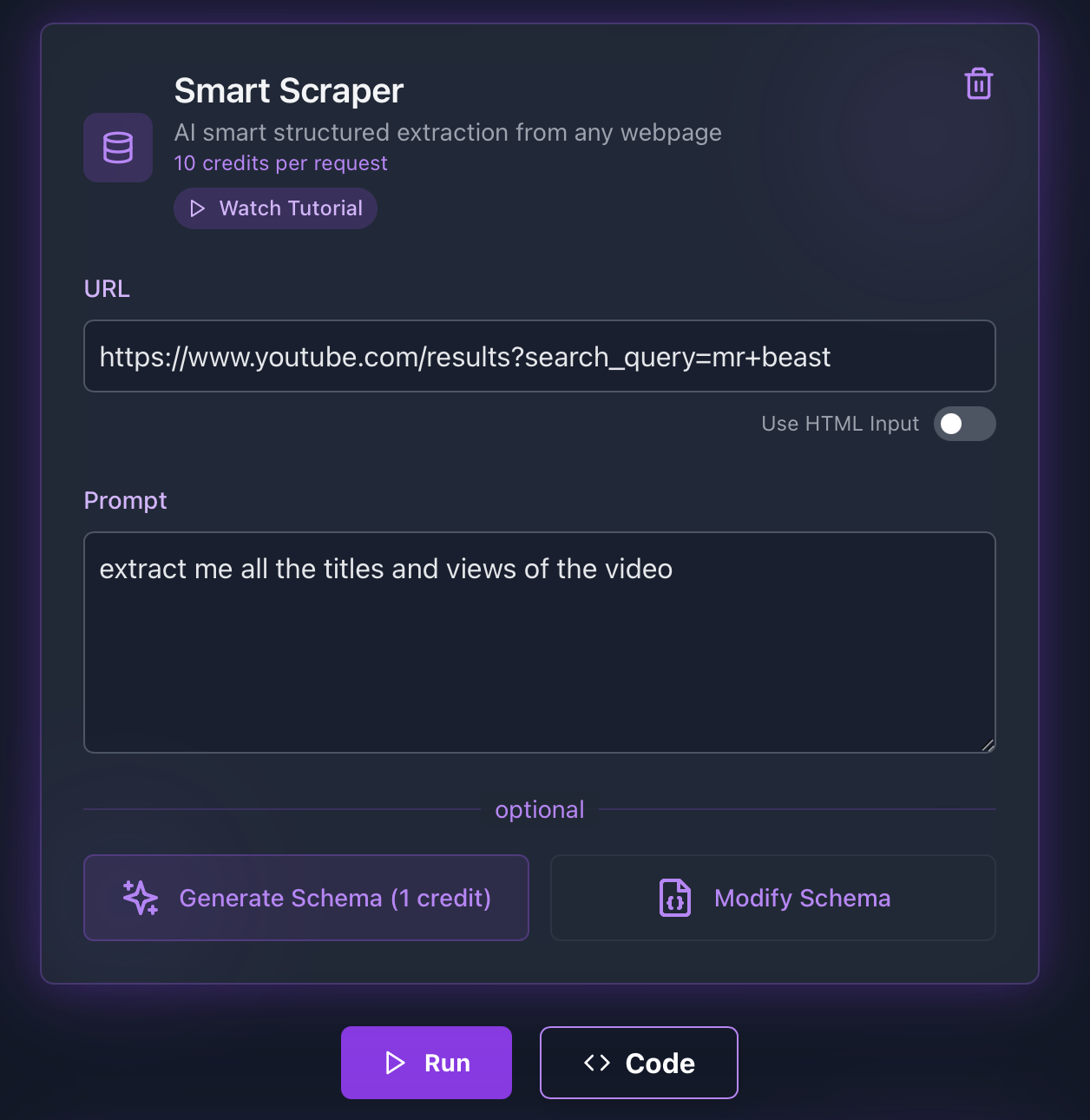
ScrapeGraphAI streamlines the process of extracting data from YouTube. Below are examples in different programming languages showing how to scrape YouTube videos, including titles and view counts from search results:
Python Example
pythonfrom scrapegraph_py import Client from scrapegraph_py.logger import sgai_logger sgai_logger.set_logging(level="INFO") # Initialize the client sgai_client = Client(api_key="sgai-********************") # SmartScraper request response = sgai_client.smartscraper( website_url="https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=mr+beast", user_prompt="extract me all the titles and views of the video" ) # Print the response print(f"Request ID: {response['request_id']}") print(f"Result: {response['result']}") sgai_client.close()
JavaScript Example
javascriptimport { Client } from 'scrapegraph-js'; import { z } from 'zod'; // Define the schema const videoSchema = z.object({ title: z.string(), views: z.string() }); type VideoSchema = z.infer<typeof videoSchema>; // Initialize the client const sgai_client = new Client("sgai-********************"); try { const response = await sgai_client.smartscraper({ websiteUrl: "https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=mr+beast", userPrompt: "extract me all the titles and views of the video", outputSchema: videoSchema }); console.log('Request ID:', response.requestId); console.log('Result:', response.result); } catch (error) { console.error(error); } finally { sgai_client.close(); }
cURL Example
bashcurl -X 'POST' \ 'https://api.scrapegraphai.com/v1/smartscraper' \ -H 'accept: application/json' \ -H 'SGAI-APIKEY: sgai-********************' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{ "website_url": "https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=mr+beast", "user_prompt": "extract me all the titles and views of the video", } }'
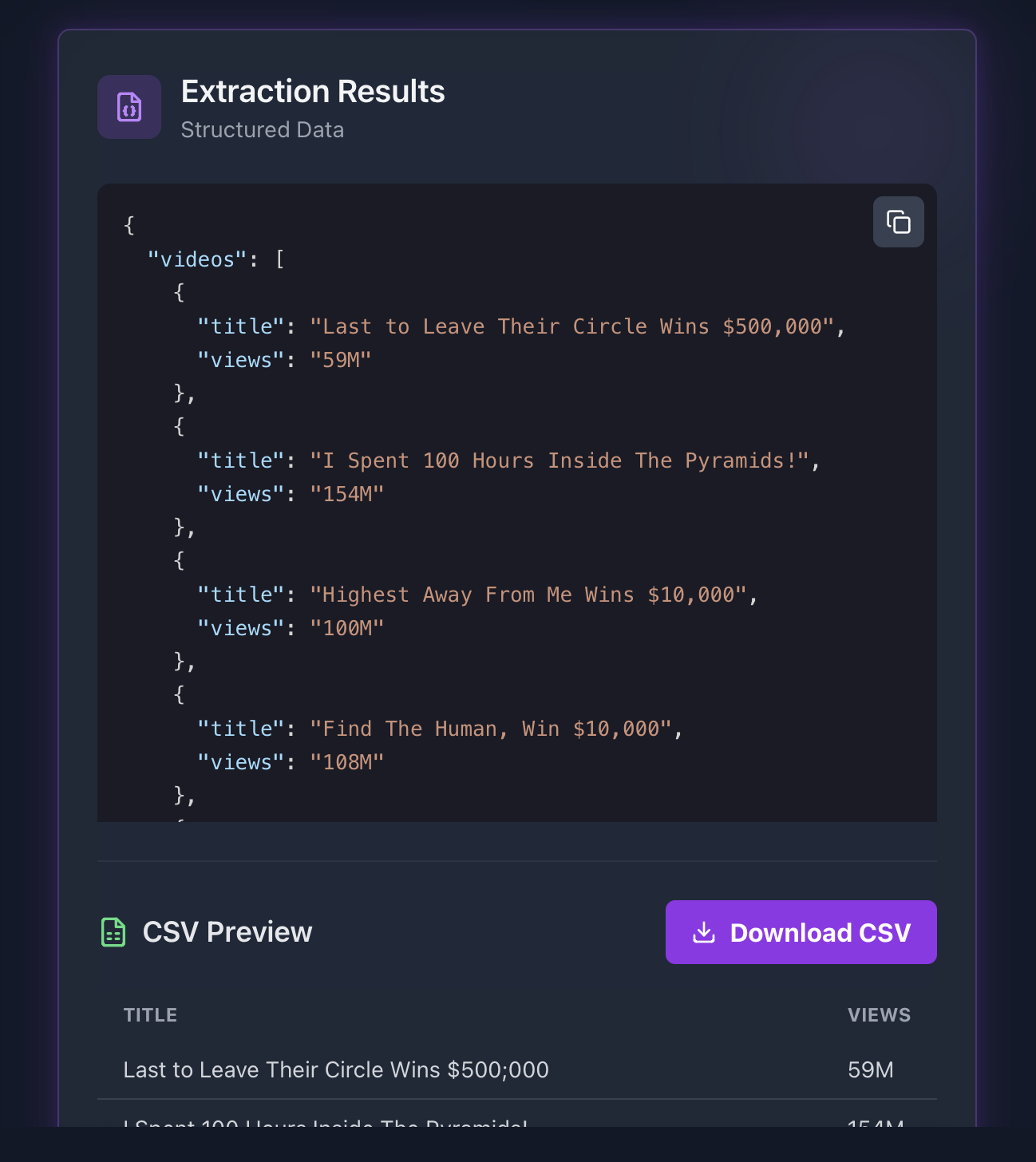
Example Response
Here's what the extracted data might look like:
json{ "videos": [ { "title": "Last to Leave Their Circle Wins $500,000", "views": "59M" }, { "title": "I Spent 100 Hours Inside The Pyramids!", "views": "154M" }, { "title": "Highest Away From Me Wins $10,000", "views": "100M" }, { "title": "Find The Human, Win $10,000", "views": "108M" }, { "title": "Find This Stranger, Win $10,000", "views": "173M" }, { "title": "Reach the Money, Win $10,000", "views": "127M" }, { "title": "Last Person Hanging Wins $10,000", "views": "188M" }, { "title": "Subscribe For An iPhone", "views": "91M" }, { "title": "Beast Games Winner Breaks Silence on $10,000,000 Prize, MrBeast, and Getting Fired", "views": "132K" }, { "title": "I Survived 50 Hours In A Maximum Security Prison", "views": "273M" }, { "title": "I got pregnant at Beast Games 🤷♀️", "views": "2.5M" }, { "title": "MrBeast Got Arrested !", "views": "18M" }, { "title": "Restocking MrBeast Labs at Walmart", "views": "137M" }, { "title": "MrBeast made fun of me..", "views": "38M" }, { "title": "First Person Who Buys My Chocolate Wins $10,000", "views": "108M" }, { "title": "Pass The Phone To…", "views": "185M" } ] }
Breaking Down the Code
- Client Initialization and Logging
The client is initialized with an API key, and logging is set to the "INFO" level to track the scraping process.
Ready to Scale Your Data Collection?
Join thousands of businesses using ScrapeGrapAI to automate their web scraping needs. Start your journey today with our powerful API.
-
Sending the Request
The smartscraper method is used to send a request to YouTube. The request includes a URL targeting YouTube search results for "mr beast" and a custom prompt to extract video titles and view counts. -
Handling the Response
The JSON response includes a list of videos, each with its title and view count, which is printed to the console. -
Closing the Client
Once the operation is complete, the client is closed to free up system resources.
Benefits of Using ScrapeGraphAI
- Ease of Use: Quickly set up scraping tasks with minimal code.
- Customization: Tailor your scraping requests with custom prompts to extract specific data.
- Efficiency: Handle large volumes of data swiftly and reliably.
Frequently Asked Questions
What data can I extract from YouTube?
Extractable data includes:
- Video titles
- View counts
- Channel information
- Comments
- Engagement metrics
- Video details
How do I handle YouTube's terms of service?
Considerations include:
- Rate limiting
- Data usage
- Privacy compliance
- Terms of service
- Ethical guidelines
- Legal requirements
What are the common challenges?
Common challenges include:
- Dynamic content
- Rate limiting
- Anti-bot measures
- Data validation
- Structure changes
- Performance issues
How do I ensure data accuracy?
Accuracy measures:
- Data validation
- Cross-checking
- Error handling
- Quality control
- Monitoring
- Testing
What are the best practices?
Best practices include:
- Rate limiting
- Error handling
- Data validation
- Resource management
- Documentation
- Testing
How do I handle errors?
Error handling includes:
- API errors
- Network issues
- Timeout handling
- Retry mechanisms
- Logging
- Recovery
What about performance?
Performance considerations:
- Resource management
- Caching
- Parallel processing
- Error handling
- Monitoring
- Optimization
How do I scale the solution?
Scaling strategies:
- Resource optimization
- Load balancing
- Error handling
- Monitoring
- Documentation
- Testing
What about data storage?
Storage considerations:
- Database selection
- Data organization
- Backup strategies
- Access control
- Security
- Maintenance
How do I keep the solution updated?
Maintenance includes:
- Regular updates
- Bug fixes
- Feature additions
- Documentation
- Testing
- Optimization
What Can You Scrape from YouTube?
When you scrape YouTube, you can extract various types of data:
-
Video Information:
- Titles and descriptions
- View counts and engagement metrics
- Upload dates and duration
- Video quality and format details
-
Channel Data:
- Subscriber counts
- Channel statistics
- Upload frequency
- Channel performance metrics
-
User Engagement:
- Comments and replies
- Like/dislike ratios
- Share counts
- User interactions
Best Practices for YouTube Scraping
When you scrape YouTube, follow these best practices:
-
Respect Rate Limits:
- Implement proper delays between requests
- Use appropriate scraping intervals
- Monitor API usage
-
Data Validation:
- Verify extracted data accuracy
- Implement error handling
- Cross-check results
-
Ethical Considerations:
- Follow YouTube's terms of service
- Respect user privacy
- Use data responsibly
Conclusion
Learning how to scrape YouTube data with ScrapeGraphAI enables you to gather valuable insights into video performance and trends, thereby enhancing your content strategy and marketing decisions. By automating data extraction, you can stay ahead in a competitive digital landscape.
Start scraping YouTube today and unlock the power of data-driven content creation!
Happy scraping!
Related Resources
Want to learn more about YouTube data extraction? Explore these guides:
- Web Scraping 101 - Master the basics of web scraping
- AI Agent Web Scraping - Learn about AI-powered scraping
- Mastering ScrapeGraphAI - Deep dive into our scraping platform
- Building Intelligent Agents - Create powerful automation agents
- Pre-AI to Post-AI Scraping - See how AI has transformed automation
- Structured Output - Learn about data formatting
- Data Innovation - Discover innovative data methods
- Full Stack Development - Build complete data solutions
- Web Scraping Legality - Understand legal considerations