Web scraping is an essential skill for data collection, market research, price monitoring, and competitive analysis. However, building scrapers from scratch can be complex and time-consuming. This is where n8n comes in—a powerful workflow automation tool that makes web scraping accessible without writing complex code.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll show you how to build a web scraper using n8n. We'll use Amazon as a practical example, but the techniques you'll learn can be applied to scrape any website. You'll learn how to extract product names, prices, ratings, and other data from web pages.
Getting Started with n8n
Before diving into the scraping workflow, let's take a look at the n8n interface. n8n provides an intuitive visual workflow builder that makes it easy to create automation workflows without writing complex code.
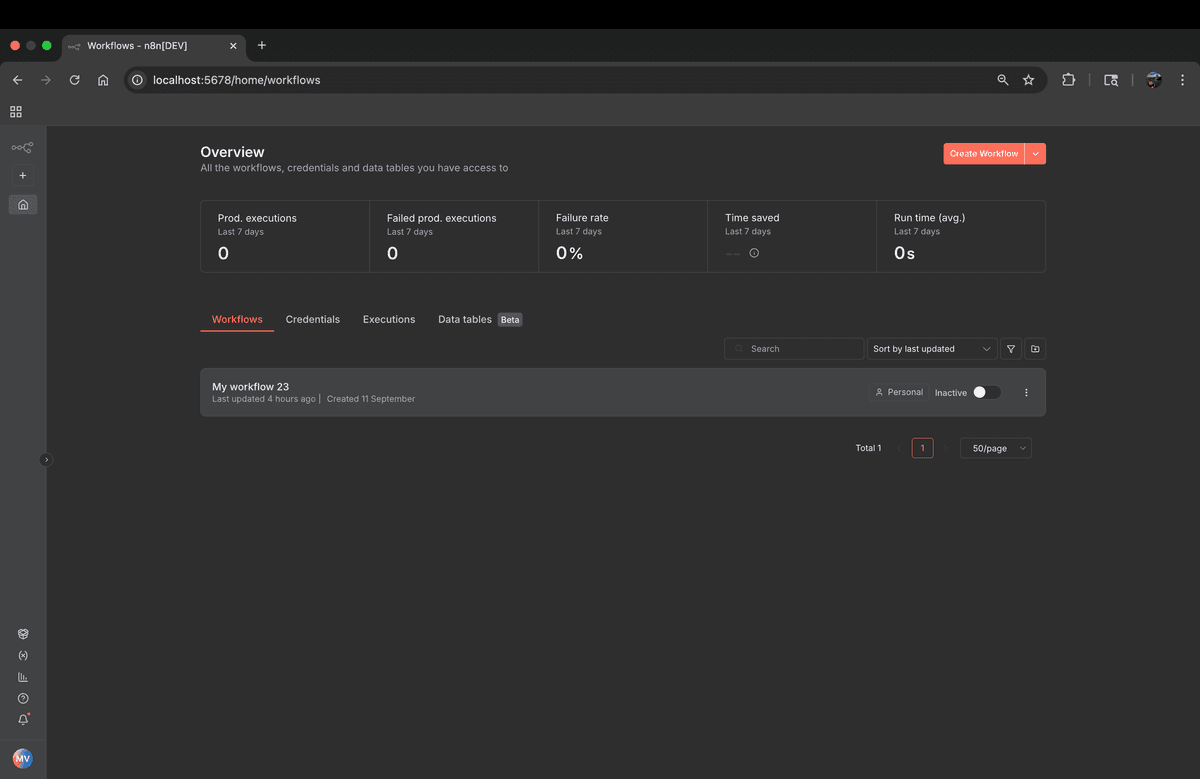
What is n8n?
n8n is an open-source workflow automation tool that allows you to connect different services and automate tasks without writing complex code. It provides a visual interface where you can create workflows by connecting nodes, making it perfect for web scraping, data extraction, and automation tasks.
Key Features of n8n:
- Visual Workflow Builder: Create workflows with a drag-and-drop interface
- Extensive Node Library: Access to hundreds of pre-built integrations
- Self-Hosted or Cloud: Deploy on your own infrastructure or use n8n Cloud
- HTTP Request Nodes: Built-in support for web scraping and API calls
- Data Transformation: Built-in nodes for processing and transforming data
Why Build a Web Scraper?
Web scraping enables you to extract valuable data from websites for various purposes:
- Price Monitoring: Track product prices over time to identify trends and opportunities
- Competitive Analysis: Monitor competitor products, pricing, and customer reviews
- Market Research: Analyze product categories, trends, and customer preferences
- Data Collection: Gather information for research, analysis, and decision-making
- Content Aggregation: Collect data from multiple sources for content creation
- SEO and Analytics: Extract data for SEO analysis and performance tracking
In this tutorial, we'll use Amazon as a practical example. Here's what an Amazon search results page looks like—notice the product cards containing titles, prices, ratings, and other valuable information that we'll extract using n8n. The same techniques can be applied to any website.

Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have:
- n8n Installed: You can use n8n Cloud or self-host n8n
- Basic Understanding: Familiarity with n8n's interface and workflow concepts
- Target URL: The webpage you want to scrape (we'll use an Amazon search results page as an example)
Setting Up Your n8n Web Scraper Workflow
Let's create a web scraping workflow step by step. We'll use Amazon search results as a practical example, but you can adapt these steps to scrape any website. We'll use the following URL:
https://www.amazon.com/s?k=watc&crid=ANQU8C01KRIK&sprefix=watc%2Caps%2C395&ref=nb_sb_noss_2
Step 1: Create a New Workflow
- Open your n8n instance
- Click "New Workflow"
- Give it a descriptive name like "Web Scraper" or "Product Data Extractor"
Step 2: Add HTTP Request Node
The HTTP Request node is the core of any web scraping workflow. It fetches the HTML content from your target website.
- Click the "+" button to add a node
- Search for "HTTP Request" and select it
- Configure the node with the following settings:
Method: GET
URL: Enter the URL of the webpage you want to scrape (in our example: https://www.amazon.com/s?k=watc&crid=ANQU8C01KRIK&sprefix=watc%2Caps%2C395&ref=nb_sb_noss_2)
Headers (important for avoiding blocks and appearing as a real browser):
{
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML,
like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"Accept":
"text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8",
"Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.5",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate, br",
"Connection": "keep-alive",
"Upgrade-Insecure-Requests": "1"
}
Here's how the HTTP Request node should be configured in n8n. Make sure to set the method to GET, paste your target URL, and add the headers as shown above to avoid being blocked by anti-bot measures. These headers make your requests appear as if they're coming from a real browser.
Step 3: Parse HTML Content
Most websites have complex HTML structures. We'll use n8n's HTML Extract node or Code node to parse and extract the data we need. For our Amazon example, we'll extract product information, but you can adapt these selectors to any website.
Option A: Using HTML Extract Node (Recommended)
- Add an "HTML Extract" node after the HTTP Request node
- Connect the HTTP Request node to the HTML Extract node
- Configure the extraction rules:
{
"fields": [
{
"key": "product_title",
"selector": "h2.a-size-mini a span",
"attribute": "text"
},
{
"key": "product_price",
"selector": ".a-price .a-offscreen",
"attribute": "text"
},
{
"key": "product_rating",
"selector": ".a-icon-alt",
"attribute": "text"
},
{
"key": "product_reviews",
"selector": ".a-size-base",
"attribute": "text"
},
{
"key": "product_url",
"selector": "h2.a-size-mini a",
"attribute": "href"
}
]
}Option B: Using Code Node (JavaScript)
If you need more control, use a Code node with JavaScript:
// Get the HTML from the previous node
const html = $input.item.json.body;
// Use a simple regex or string manipulation
// Note: For production, consider using a proper HTML parser
const products = [];
// Extract product titles (simplified example)
const titleMatches = html.match(/<h2[^>]*>[\s\S]*?<span[^>]*>([^<]+)<\/span>/g);
if (titleMatches) {
titleMatches.forEach((match, index) => {
const title = match.match(/<span[^>]*>([^<]+)<\/span>/)[1];
products.push({
title: title.trim(),
index: index
});
});
}
return products.map(product => ({
json: product
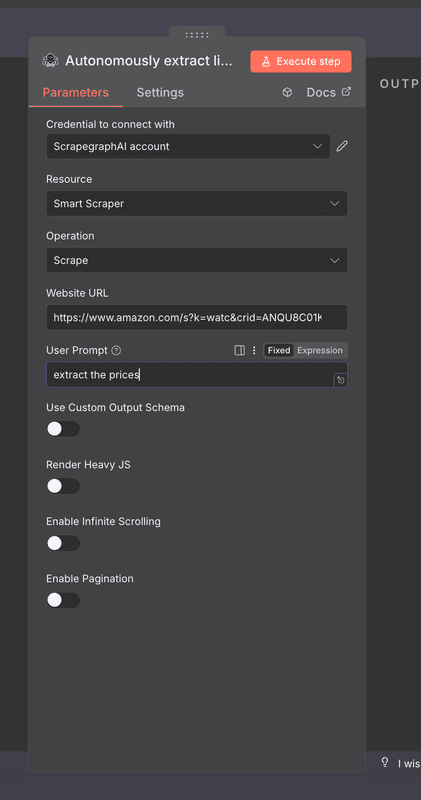
}));After setting up the HTTP Request node, you'll need to parse the HTML content. The HTML Extract node allows you to define CSS selectors to extract specific data fields from any webpage. Here's an example configuration showing how to extract product titles, prices, ratings, and other information from our Amazon example. You'll need to inspect your target website's HTML structure to find the appropriate selectors.
Step 4: Transform and Clean Data
Add a "Set" node to transform and structure your data:
- Add a "Set" node after the HTML Extract node
- Map the extracted fields to clean output:
{
"product_name": "={{ $json.product_title }}",
"price": "={{ $json.product_price }}",
"rating": "={{ $json.product_rating }}",
"review_count": "={{ $json.product_reviews }}",
"url": "={{ 'https://www.amazon.com' + $json.product_url }}",
"scraped_at": "={{ $now }}"
}Step 5: Handle Pagination (Optional)
To scrape multiple pages from a website, add pagination handling:
- Add a "Split In Batches" node or use a Loop node
- Add an "HTTP Request" node inside the loop
- Modify the URL to include page parameters (the exact format depends on the website):
For Amazon:
https://www.amazon.com/s?k=watc&page={{ $json.page_number }}
For other sites, you might use:
?page={{ $json.page_number }}&p={{ $json.page_number }}- Or other pagination patterns specific to your target site
Step 6: Store the Data
Finally, save your scraped data. You can:
Option A: Save to Google Sheets
- Add a "Google Sheets" node
- Configure your spreadsheet credentials
- Map the fields to columns
Option B: Save to Database
- Add a database node (PostgreSQL, MySQL, etc.)
- Configure connection
- Insert the scraped data
Option C: Export to JSON/CSV
- Add a "Write Binary File" node
- Format data as JSON or CSV
- Save to your desired location
Once you've completed all the steps, your n8n workflow should look something like this. This complete workflow shows the flow from fetching the webpage, extracting the data, transforming it, and finally storing it in your chosen destination.
Complete Workflow Example
Here's a complete workflow structure for web scraping that you can adapt to any website:
1. HTTP Request (Fetch target webpage)
↓
2. HTML Extract (Parse and extract data)
↓
3. Set (Transform and clean data)
↓
4. Split In Batches (Handle multiple items)
↓
5. Google Sheets / Database (Store data)
This structure works for scraping any website—just adjust the URL, selectors, and data transformation logic based on your target site.
Advanced Techniques
Handling JavaScript Rendered Content
Many modern websites use JavaScript to load content dynamically. For these sites, you'll need to render JavaScript before extraction:
- Use Playwright/Puppeteer: Add a "Playwright" or "Puppeteer" node to render JavaScript
- Wait for Elements: Configure the node to wait for specific selectors to appear
- Extract After Rendering: Use HTML Extract after the page is fully loaded
Rate Limiting and Delays
To avoid being blocked by websites:
- Add a "Wait" node between requests
- Set random delays (2-5 seconds) to mimic human behavior
- Use proxy rotation if scraping at scale
- Respect the website's robots.txt file
Error Handling
Add error handling to your workflow:
- Add an "IF" node to check for errors
- Add retry logic with "Retry on Fail" option
- Log errors to a separate location
Best Practices for Web Scraping with n8n
- Respect Rate Limits: Add delays between requests to avoid IP bans
- Use Proper Headers: Always include realistic browser headers to appear as a legitimate user
- Handle Errors Gracefully: Implement retry logic and error logging for robust workflows
- Validate Data: Check that extracted data is complete and accurate before storing
- Monitor Your Workflows: Set up alerts for failed executions to catch issues early
- Respect robots.txt: Check the website's robots.txt file for scraping guidelines
- Use Proxies for Scale: Consider proxy rotation for large-scale scraping operations
- Cache When Possible: Store intermediate results to avoid re-scraping the same content
- Inspect HTML Structure: Use browser developer tools to find reliable CSS selectors
- Test Selectors: Regularly test your selectors as websites may change their HTML structure
Legal and Ethical Considerations
⚠️ Important: Before scraping any website, consider:
- Terms of Service: Review the website's Terms of Service regarding data scraping
- Rate Limiting: Don't overload servers with too many requests
- Legal Compliance: Ensure your scraping activities comply with local laws and regulations
- Data Usage: Use scraped data responsibly and ethically
- Respect Privacy: Don't scrape personal information or violate privacy laws
- Copyright: Be aware of copyright restrictions on the content you're scraping
- Public Data Only: Only scrape publicly available data, not protected or private content
Common Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Websites Block Requests
Solution:
- Use realistic User-Agent headers that mimic real browsers
- Add delays between requests to avoid rate limiting
- Rotate IP addresses using proxies for large-scale operations
- Consider using official APIs when available (e.g., Amazon Product Advertising API)
Challenge 2: Dynamic Content Loading
Solution:
- Use Playwright or Puppeteer nodes to render JavaScript
- Wait for specific elements to appear before extraction
- Use n8n's browser automation capabilities
- Monitor network requests to understand when content loads
Challenge 3: Changing HTML Structure
Solution:
- Use more flexible CSS selectors (avoid overly specific paths)
- Implement fallback extraction methods
- Regularly test and update your workflows
- Consider using AI-powered extraction tools like ScrapeGraphAI that adapt to changes
- Use multiple selector strategies for critical data
Challenge 4: Large-Scale Scraping
Solution:
- Use n8n's queue system for parallel processing
- Implement pagination handling
- Use database storage for efficiency
- Consider distributed n8n instances
Alternative: Using ScrapeGraphAI with n8n
For more reliable and maintenance-free web scraping, you can integrate ScrapeGraphAI with n8n. This approach uses AI to understand webpage content and extract data using natural language prompts, making it more resilient to HTML structure changes.
- Add an "HTTP Request" node
- Configure it to call ScrapeGraphAI's API
- Use natural language prompts to extract data (no CSS selectors needed!)
Example n8n HTTP Request Configuration:
{
"method": "POST",
"url": "https://api.scrapegraphai.com/v1/smartscraper",
"headers": {
"SGAI-APIKEY": "your-api-key",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
"body": {
"website_url":
"https://www.amazon.com/s?k=watc&crid=ANQU8C01KRIK&sprefix=watc%2Caps%2C395&ref=nb_sb_noss_2",
"user_prompt": "Extract all product names, prices, ratings, and review counts from
the search results"
}
}
This approach is more resilient to HTML structure changes and requires less maintenance than traditional selector-based scraping.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I scrape websites legally with n8n?
The legality depends on your use case, jurisdiction, and the website's Terms of Service. Always review the website's ToS and consult legal advice if needed. For commercial use, consider using official APIs when available.
How often can I scrape a website?
There's no fixed limit, but websites may block your IP if you make too many requests too quickly. Add delays (2-5 seconds) between requests and monitor for blocks. Respect the website's rate limits and robots.txt file.
Do I need proxies?
For small scale scraping, proxies may not be necessary. For large scale operations, proxy rotation is recommended to avoid IP bans.
Can n8n handle JavaScript-heavy pages?
Yes, n8n supports Playwright and Puppeteer nodes that can render JavaScript before extraction.
How do I handle pagination?
Use n8n's Loop nodes or "Split In Batches" to iterate through multiple pages. Modify the URL parameters for each page.
What's the difference between n8n and ScrapeGraphAI?
- n8n: Workflow automation tool that requires manual HTML parsing and selector configuration
- ScrapeGraphAI: AI-powered scraping that uses natural language prompts and adapts to HTML changes automatically
Can I schedule web scraping workflows?
Yes, n8n supports scheduling with Cron nodes. You can set up workflows to run automatically at specified intervals (hourly, daily, weekly, etc.).
How do I store scraped data?
You can store data in various ways:
- Google Sheets (using Google Sheets node)
- Databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB nodes)
- Cloud storage (AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage)
- Local files (Write Binary File node)
- APIs (send data to external services)
Conclusion
Building web scrapers with n8n provides a powerful way to automate data collection for market research, price monitoring, competitive analysis, and more. By following this guide, you can create robust workflows that extract information from any website efficiently.
Remember to:
- Respect rate limits and the website's Terms of Service
- Implement proper error handling and retry logic
- Use realistic headers and delays to avoid blocks
- Consider legal and ethical implications of your scraping activities
- Test your workflows regularly as websites may change their structure
For more advanced use cases or when you need AI-powered extraction that adapts to HTML changes automatically, consider integrating ScrapeGraphAI with your n8n workflows.
Ready to start scraping? Set up your n8n workflow today and unlock the power of automated web data collection!
Happy scraping!
Related Resources
Want to learn more about web scraping and automation? Explore these guides:
- Web Scraping 101 - Master the basics of web scraping
- AI Agent Web Scraping - Learn about AI-powered scraping
- Mastering ScrapeGraphAI - Deep dive into our scraping platform
- Effortlessly Scrape E-commerce with AI - Learn AI-powered e-commerce scraping
- Building Intelligent Agents - Create powerful automation agents
- Pre-AI to Post-AI Scraping - See how AI has transformed automation
- Structured Output - Learn about data formatting
- Web Scraping Legality - Understand legal considerations
- Zero to Production Scraping Pipeline - Build production-ready scrapers
